How to enable binary logging on an Amazon RDS read replica
Tags:
Technical Track,
12C
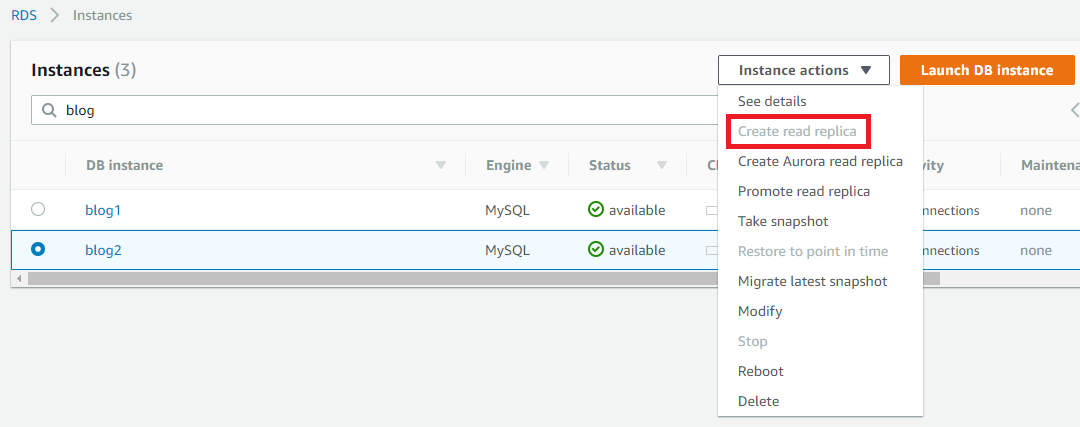
One of the more common struggles I’ve had to assist with in regard to Amazon RDS is enabling binary logging on read replicas, or forming multi-tier replication in instances using version 5.6 or later after seeing that multi-tier replication is not supported in version 5.5 (for a reason that will become clear by the end of this post.) First off, let’s have a look at the topology that I have in place in my AWS account. As you’ll see below I have a master, blog1, and a read replica that I created via the AWS console called blog2. You’ll also notice that, despite being supported, if I select instance actions while having blog2 highlighted the option to create a read replica is grayed out.
 Further, if we use the MySQL CLI to connect to blog2 and check the global variables for log_bin and binlog_format, you’ll see that binary logging is off and binlog_format is set to statement. This is strange considering that the parameter group that’s assigned to blog2 is the same as blog1 where binary logging is enabled and the format is set to mixed. In fact, when you try to change the binary logging format in the MySQL RDS parameter group you’ll see that statement isn’t even an option.
Further, if we use the MySQL CLI to connect to blog2 and check the global variables for log_bin and binlog_format, you’ll see that binary logging is off and binlog_format is set to statement. This is strange considering that the parameter group that’s assigned to blog2 is the same as blog1 where binary logging is enabled and the format is set to mixed. In fact, when you try to change the binary logging format in the MySQL RDS parameter group you’ll see that statement isn’t even an option.
 Further, if we use the MySQL CLI to connect to blog2 and check the global variables for log_bin and binlog_format, you’ll see that binary logging is off and binlog_format is set to statement. This is strange considering that the parameter group that’s assigned to blog2 is the same as blog1 where binary logging is enabled and the format is set to mixed. In fact, when you try to change the binary logging format in the MySQL RDS parameter group you’ll see that statement isn’t even an option.
Further, if we use the MySQL CLI to connect to blog2 and check the global variables for log_bin and binlog_format, you’ll see that binary logging is off and binlog_format is set to statement. This is strange considering that the parameter group that’s assigned to blog2 is the same as blog1 where binary logging is enabled and the format is set to mixed. In fact, when you try to change the binary logging format in the MySQL RDS parameter group you’ll see that statement isn’t even an option.
mysql> show global variables like 'log_bin'; show global variables like 'binlog_format';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| log_bin | OFF |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.06 sec)
+---------------+-----------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-----------+
| binlog_format | STATEMENT |
+---------------+-----------+
1 row in set (0.05 sec) So what gives? The status of the variables in our instance clearly don’t reflect the intended configuration. The answer here is to enable automatic backups for blog2. When you first create a read replica in RDS you won’t have the option to enable automatic backups and, much like this situation, you’ll have to go back and modify the read replica instance after its creation to enable automatic backups. The supporting documentation for this can be found
here. The appropriate text is as follows:
When creating a Read Replica, there are a few things to consider. First, you must enable automatic backups on the source DB instance by setting the backup retention period to a value other than 0. This requirement also applies to a Read Replica that is the source DB instance for another Read Replica. For MySQL DB instances, automatic backups are supported only for Read Replicas running MySQL 5.6 and later, but not for MySQL versions 5.5. To enable automatic backups on an Amazon RDS MySQL version 5.6 and later Read Replica, first create the Read Replica, then modify the Read Replica to enable automatic backups. After you enable automatic backups by modifying your read replica instance to have a backup retention period greater than 0 days, you’ll find that the log_bin and binlog_format will align itself with the configuration specified in your parameter group dynamically and will not require the RDS instance to be restarted. You will also be able to create a read replica from your read replica instance with no further modification requirements.

