How to creates Kubernetes jobs with Python
In this blog post I will do a quick guide, with some code examples, on how to deploy a Kubernetes Job programmatically, using Python as the language of choice. For this I’m using GKE (Google Kubernetes Engine), logging via StackTrace and haveana image available on Google Container Registry. The architecture should be something like this:
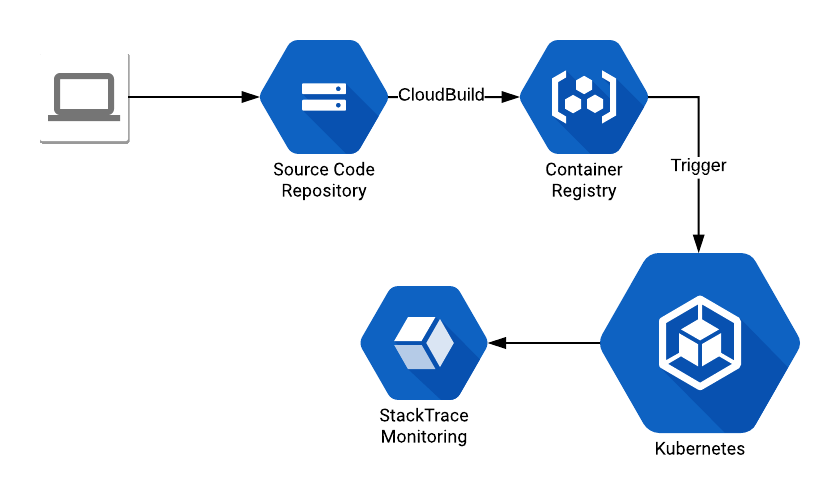 The code that I created:
The code that I created:
 The code that I created:
The code that I created:
- A Dockerfile for my container
- A Python App that has the code to run (this will be the Job)
- Commit the code to the GCP Source Code Repositories
- A CloudBuild trigger (docs: https://cloud.google.com/cloud-build/docs/) that creates the container
- Create a trigger (can be a CronJob) that runs the code that deploys the Job.
- For this exercise, I’m going to trigger the Job creation from my own laptop.
- Job object
- Contains a metadata object
- Contains a job spec object
- Contains a pod template object
- Contains a pod template spec object
- Contains a container object
- Contains a pod template spec object
- Contains a pod template object

